用 antd 做个人博客卡到前端了,迫不得已来学 react,也是干上全栈了– –学自尚硅谷张天禹 react
React 就是 js 框架,可以理解为对 js 做了封装,那么封装后的肯定用起来更方便。
相关 JS 库
- react.js:React 核心库。
- react-dom.js:提供操作 DOM 的 react 扩展库。
- babel.min.js:解析 JSX 语法代码转为 JS 代码的库。
浏览器不能直接解析 JSX 代码, 需要 babel 转译为纯 JS 的代码才能运行。只要用了 JSX,都要加上 type=“text/babel”, 声明需要 babel 来处理。
JS 库示例 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>1_使用jsx创建虚拟DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个"容器" -->
<div id="test"></div>
<!-- 引入react核心库 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入react-dom,用于支持react操作DOM -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入babel,用于将jsx转为js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel" > /* 此处一定要写babel */
//1.创建虚拟DOM
const VDOM = ( /* 此处一定不要写引号,因为不是字符串 */
<h1 id="title">
<span>Hello,React</span>
</h1>
)
//2.渲染虚拟DOM到页面
ReactDOM.render(VDOM,document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
浏览器控制台可能会报如下错误:
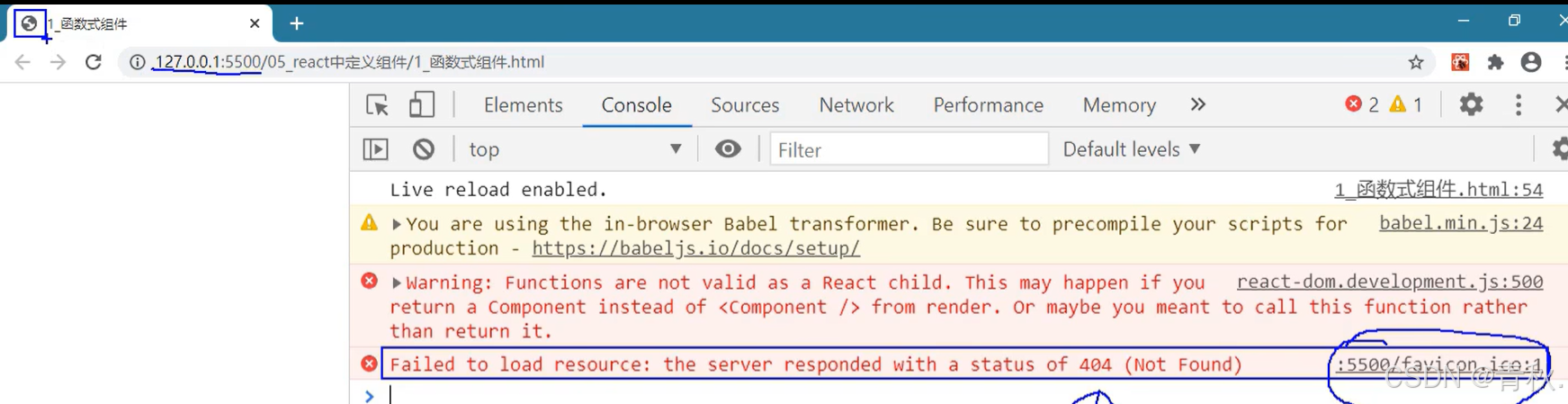
找不到 favicon.ico 的资源,那么左上角的标签页就不显示图标。解决方法是在项目中根目录下放一个同名图标即可。
真实 DOM 和虚拟 DOM
React 提供了一些 API 来创建虚拟 DOM 对象
虚拟 dom 定义在<script type=“text/babel”> </script>中!!!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
//创建虚拟dom
1.用React创建,语法:React.createElement('标签名',{标签属性},'标签内容')
const VDOM = React.createElement('Good',{id:'title'},'Hello JSX')
2.用JSX语法创建,可以看到这样创建dom更简单
const VDOM = <Good id="title">Hello JSX</Good>
//创建真实dom,不常用
const DOM = document.createElement()
|
- 我们编码时基本只需要操作 react 的虚拟 DOM 相关数据, react 会转换为真实 DOM 变化而更新界。
- 虚拟 DOM 对象最终都会被 React 转换为真实的 DOM。
- 虚拟 dom 本质是一个 Object(控制台输出 VDOM instanceof Object 的结果为 true)。
- 虚拟 dom 内部元素少,真实 dom 内部元素多,因为虚拟 dom 是 react 内用,无需真实 dom 那么多属性。
注意!创建的虚拟 dom 只能有一个根标签,并且内部的标签必须闭合(有 /> 结束),如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
//正确的创建虚拟DOM,根标签只有一个
const VDOM = (
<div>
<h2>青秋</h2>
</div>
)
//错误的创建虚拟DOM,根标签有俩div
const VDOM = (
<div>
<h2>青秋</h2>
</div>
<div>
<h2>青秋</h2>
</div>
)
//必须有/>结束
const VDOM = (
<div>
<h2>青秋</h2>
//<input type="text" > 错误,没有闭合
<input type="text"/> 或 <input type="text"/> </input>
</div>
)
|
JSX 语法规则
全称是 JavaScript XML,是 react 定义的一种类似于 XML 的 JS 扩展语法,可以把 js 和 html 写在一起,类似 JSP。
JS + XML 本质是React.createElement ( component , props , … children **)**方法的语法糖
-
作用: 用来简化创建虚拟 DOM
-
写法:var VDOM = <h1> Hello JSX</h1>
-
注意:这样创建的<h1>不是字符串, 也不是 HTML/XML 标签,它最终产生的就是一个 JS 对象
-
标签名和标签属性任意,可以是 HTML 标签属性或其它
-
语法规则:
-
遇到 < 开头的代码, 以标签的语法解析: 与 html 同名标签则转换为 html 同名元素 , 其它标签需要特别解析,如:
1
2
3
4
5
|
//自定义的h1会被替换成html中同名的标签<h1>
const vdom1 = <h1>hello</h1>;
//自定义的Good在html中不存在同名标签,浏览器控制台会报错
const vdom2 = <good>hello</good>;
|
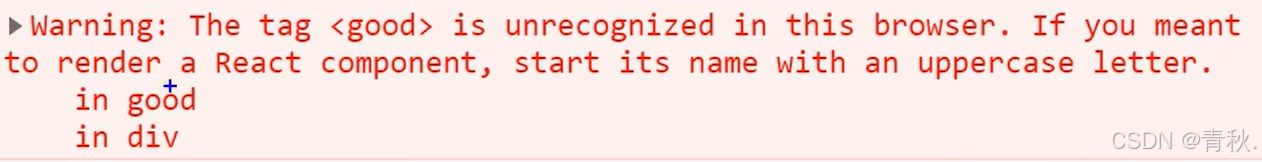 也就是说,定义的虚拟 dom 中,开头小写的标签会去 html 中寻找同名的元素并替换,找不到就会报上面的错误。如果是开头大写的标签,那么就是自定义的组件 ,如果写成 Good,那么浏览器就会去渲染 Good 组件,因此 Good 组件需要提前定义,否则会 undefined。
也就是说,定义的虚拟 dom 中,开头小写的标签会去 html 中寻找同名的元素并替换,找不到就会报上面的错误。如果是开头大写的标签,那么就是自定义的组件 ,如果写成 Good,那么浏览器就会去渲染 Good 组件,因此 Good 组件需要提前定义,否则会 undefined。
虚拟 DOM 中使用内联样式
在虚拟 dom 中使用内联样式(直接在标签中写 style),需要用{{ }}包裹,其中外层的{ }代表标签里要写 js 表达式,内层的{ }代表要写的是一个对象。
另外{{ }}的 style 属性名是小驼峰的形式,比如 font-size 写成 fontSize。真实 dom 的类名是 class,**虚拟 dom 的类名是 className。**如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//真实dom内联样式
<div class='dom'>
<h2 style='color: black;font-size: large;'>青秋博客</h2>
</div>;
//虚拟DOM内联样式
const VDOM = (
<div className='vdom'>
<h2 style={{ color: 'white', fontSize: '29px' }}>青秋博客</h2>
</div>
);
|
render 渲染虚拟 DOM
语法: ReactDOM . render (<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById(’test’))
作用: 将定义的虚拟 DOM 元素渲染到页面中的真实 DOM 中显示。
参数说明:MyComponent**是创建的虚拟 dom 对象;**document.getElementById(’test’)是根据 id 获取的真实 dom 容器,是用来用来包含虚拟 dom 的。
函数式组件和类式组件
简单组件
组件名必须首字母大写!!小写则会去 html 中寻找同名元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<script type="text/babel">
//1.创建函数式组件
function MyComponent(){
console.log(this); //此处的this是undefined,因为babel编译后开启了严格模式
return <h2>我是用函数定义的组件(适用于【简单组件】的定义)</h2>
}
//2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById('test'))
/*
执行了ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>.......之后,发生了什么?
1.React解析组件标签,找到了MyComponent组件。
2.发现组件是使用函数定义的,随后调用该函数,将返回的虚拟DOM转为真实DOM,随后呈现在页面中。
*/
</script>
|
复杂组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
<script type="text/babel">
//1.创建类式组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render(){
//render是放在哪里的?------ MyComponent的原型对象上,供实例使用。
//render中的this是谁?------ MyComponent的实例对象 <=> MyComponent组件实例对象。
console.log('render中的this:',this);
return <h2>我是用类定义的组件(适用于【复杂组件】的定义)</h2>
}
}
//2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>,document.getElementById('test'))
/*
执行了ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent/>.......之后,发生了什么?
1.React解析组件标签,找到了MyComponent组件。
2.发现组件是使用类定义的,随后new出来该类的实例,并通过该实例调用到原型上的render方法。
3.将render返回的虚拟DOM转为真实DOM,随后呈现在页面中。
*/
</script>
|
State 状态
类的基本知识
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>1_类的基本知识</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" >
/*
总结:
1.类中的构造器不是必须要写的,要对实例进行一些初始化的操作,如添加指定属性时才写。
2.如果A类继承了B类,且A类中写了构造器,那么A类构造器中的super是必须要调用的。
3.类中所定义的方法,都放在了类的原型对象上,供实例去使用。
*/
//创建一个Person类
class Person {
//构造器方法
constructor(name,age){
//构造器中的this是谁?------ 类的实例对象
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
//一般方法
speak(){
//speak方法放在了哪里?------类的原型对象上,供实例使用
//通过Person实例调用speak时,speak中的this就是Person实例
console.log(`我叫${this.name},我年龄是${this.age}`);
}
}
//创建一个Student类,继承于Person类
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name,age,grade){
super(name,age)
this.grade = grade
this.school = '门头沟大学'
}
//重写从父类继承过来的方法
speak(){
console.log(`我叫${this.name},我年龄是${this.age},我读的是${this.grade}年级`);
this.study()
}
study(){
//study方法放在了哪里?------类的原型对象上,供实例使用
//通过Student实例调用study时,study中的this就是Student实例
console.log('我很努力的学习');
}
}
class Car {
constructor(name,price){
this.name = name
this.price = price
// this.wheel = 4
}
//类中可以直接写赋值语句,如下代码的含义是:给Car的实例对象添加一个属性,名为a,值为1
a = 1
wheel = 4
static demo = 100
}
const c1 = new Car('奔驰c63',199)
console.log(c1);
console.log(Car.demo);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
- 状态即数据,状态变化会驱动视图变化,可以简单理解为存储数据的对象。
- 复杂组件即类定义组件有 this,那么就有 state,可以理解为一个对象的属性,可以通过 constructor()传递参数,而简单组件的 this 是 undefined 就没有 state 一说。
- render 方法中的 this 就是组件实例对象
- 组件自定义的方法中 this 为 undefined,如何解决?
- 强制绑定 this,通过函数对象的 bind() 2.箭头函数
注意!!状态必须通过 setState 进行更新,不能直接更改。
正确的:this.setState({isHot:!isHot})
错误的:this.state.isHot = !isHot
state 复杂写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
<script type="text/babel">
//1.创建组件
class Weather extends React.Component{
//构造器调用几次? ------------ 1次
constructor(props){
console.log('constructor');
super(props)
//初始化状态
this.state = {isHot:false,wind:'微风'}
//changeWeather是自定义的,要解决changeWeather中this指向问题
//调用bind方法会生成一个新函数,然后把新函数绑定到this实例对象上并命名为change,那么this实例对象有了名为change的方法
this.change = this.changeWeather.bind(this)
}
//changeWeather调用几次? ------------ 点几次调几次
changeWeather(){
//changeWeather放在哪里? ------------ Weather的原型对象上,供实例使用
//由于changeWeather是作为onClick的回调,所以不是通过实例调用的,是直接调用
//类中的方法默认开启了局部的严格模式,所以changeWeather中的this为undefined
console.log('changeWeather');
//获取原来的isHot值
const isHot = this.state.isHot
//严重注意:状态必须通过setState进行更新,且更新是一种合并,不是替换。
this.setState({isHot:!isHot})
console.log(this);
//严重注意:状态(state)不可直接更改,下面这行就是直接更改!!!
//this.state.isHot = !isHot //这是错误的写法
}
//render调用几次? ------------ 1+n次 1是初始化的那次 n是状态更新的次数
render(){
console.log('render');
//读取状态
const {isHot,wind} = this.state
//render函数中调用该类的另一个函数changeWeather,需要用this调用,否则会找不到要调用的函数!!
return <h1 onClick={this.change}>今天天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'},{wind}</h1>
}
}
//2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Weather/>,document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
|
state 简单写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
<script type="text/babel">
//1.创建组件
class Weather extends React.Component{
//初始化状态
state = {isHot:false,wind:'微风'}
//自定义方法------------要用赋值语句的形式+箭头函数
changeWeather = ()=>{
const isHot = this.state.isHot
this.setState({isHot:!isHot})
}
render(){
const {isHot,wind} = this.state
return <h1 onClick={this.changeWeather}>今天天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'},{wind}</h1>
}
}
//2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Weather/>,document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
|
Props
props 用于父组件向子组件传递数据,props 只读无法修改()
基本使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<script type="text/babel">
//创建组件
class Person extends React.Component{
render(){
const {name,age,sex} = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄:{age+1}</li
</ul>
)
}
}
//渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="jerry" age={19} sex="男"/>,document.getElementById('test1'))
const p = {name:'老刘',age:18,sex:'女'}
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p}/>,document.getElementById('test3'))
</script>
|
类型限制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/prop-types.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
//创建组件
class Person extends React.Component{
render(){
const {name,age,sex} = this.props
//props是只读的
//this.props.name = 'jack' //此行代码会报错,因为props是只读的
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄:{age+1}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
//对标签属性进行类型、必要性的限制
Person.propTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string.isRequired, //限制name必传,且为字符串
sex:PropTypes.string,//限制sex为字符串
age:PropTypes.number,//限制age为数值
speak:PropTypes.func,//限制speak为函数
}
//指定默认标签属性值
Person.defaultProps = {
sex:'男',//sex默认值为男
age:18 //age默认值为18
}
//渲染组件到页面
function speak(){console.log('我说话了');}
ReactDOM.render(<Person name={100} speak={speak}/>,document.getElementById('test1'))
const p = {name:'老刘',age:18,sex:'女'}
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p}/>,document.getElementById('test3'))
</script>
|
订阅-发布 PubSub
订阅发布用于兄弟组件传递数据,在之前,一个父亲有两个儿子,两个儿子要通信,要借助父亲来传达消息,而现在使用发布订阅,不需要借助父亲,两个儿子可以直接通信。
如 List 和 Search 两个兄弟组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import PubSub from 'pubsub-js'
export default class List extends Component {
state = { //初始化状态
users:[], //users初始值为数组
isFirst:true, //是否为第一次打开页面
isLoading:false,//标识是否处于加载中
err:'',//存储请求相关的错误信息
}
componentDidMount(){
this.token = PubSub.subscribe('atguigu',(_,stateObj)=>{
this.setState(stateObj)
})
}
componentWillUnmount(){
PubSub.unsubscribe(this.token)
}
render() {
const {users,isFirst,isLoading,err} = this.state
return (
<div className="row">
{
isFirst ? <h2>欢迎使用,输入关键字,随后点击搜索</h2> :
isLoading ? <h2>Loading......</h2> :
err ? <h2 style={{color:'red'}}>{err}</h2> :
users.map((userObj)=>{
return (
<div key={userObj.id} className="card">
<a rel="noreferrer" href={userObj.html_url} target="_blank">
<img alt="head_portrait" src={userObj.avatar_url} style={{width:'100px'}}/>
</a>
<p className="card-text">{userObj.login}</p>
</div>
)
})
}
</div>
)
}
}
export default class Search extends Component {
search = ()=>{
//获取用户的输入(连续解构赋值+重命名)
const {keyWordElement:{value:keyWord}} = this
//发送请求前通知List更新状态
PubSub.publish('atguigu',{isFirst:false,isLoading:true})
//发送网络请求
axios.get(`/api1/search/users?q=${keyWord}`).then(
response => {
//请求成功后通知List更新状态
PubSub.publish('atguigu',{isLoading:false,users:response.data.items})
},
error => {
//请求失败后通知App更新状态
PubSub.publish('atguigu',{isLoading:false,err:error.message})
}
)
}
render() {
return (
<section className="jumbotron">
<h3 className="jumbotron-heading">搜索github用户</h3>
<div>
<input ref={c => this.keyWordElement = c} type="text" placeholder="输入关键词点击搜索"/>
<button onClick={this.search}>搜索</button>
</div>
</section>
)
}
}
|
Ref
为自定义的标签打标识
字符串形式的 ref
string 形式的 ref 存在效率问题,不推荐使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<script type="text/babel">
//创建组件
class Demo extends React.Component{
//展示左侧输入框的数据
showData = ()=>{
const {input1} = this.refs
alert(input1.value)
}
//展示右侧输入框的数据
showData2 = ()=>{
const {input2} = this.refs
alert(input2.value)
}
render(){
return(
<div>
//ref相当于属性id,即标识了一个名为input1的input标签
<input ref="input1" type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData}>点我提示左侧的数据</button>
<input ref="input2" onBlur={this.showData2} type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据"/>
</div>
)
}
}
//渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Demo a="1" b="2"/>,document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
|
回调函数的 ref
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<script type="text/babel">
//创建组件
class Demo extends React.Component{
//展示左侧输入框的数据
showData = ()=>{
const {input1} = this
alert(input1.value)
}
//展示右侧输入框的数据
showData2 = ()=>{
const {input2} = this
alert(input2.value)
}
render(){
return(
<div>
//input的ref为c,把c赋给this实例对象,即把c标识的这个input标签赋给this对象,同时把input标签命名为myinput
<input ref={c => this.myinput = c } type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData}>点我提示左侧的数据</button>
<input onBlur={this.showData2} ref={c => this.input2 = c } type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据"/>
</div>
)
}
}
//渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Demo a="1" b="2"/>,document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
|
createRef()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
<script type="text/babel">
//创建组件
class Demo extends React.Component{
/*
React.createRef调用后可以返回一个容器,该容器可以存储被ref所标识的节点,该容器是"专人专用"的
*/
myRef = React.createRef()
myRef2 = React.createRef()
//展示左侧输入框的数据
showData = ()=>{
alert(this.myRef.current.value);
}
//展示右侧输入框的数据
showData2 = ()=>{
alert(this.myRef2.current.value);
}
render(){
return(
<div>
<input ref={this.myRef} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData}>点我提示左侧的数据</button>
<input onBlur={this.showData2} ref={this.myRef2} type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据"/>
</div>
)
}
}
//渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Demo a="1" b="2"/>,document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
|
Ajax 和 Axios
前置说明
- React 本身只关注于界面, 并不包含发送 ajax 请求的代码
- 前端应用需要通过 ajax 请求与后台进行交互(json 数据)
- react 应用中需要集成第三方 ajax 库(或自己封装)
Ajax 请求库
- jQuery: 比较重, 如果需要另外引入不建议使用
- axios: 轻量级, 建议使用
- 封装 XmlHttpRequest 对象的 ajax(XHR)
- promise 风格
- 可以用在浏览器端和 node 服务器端
Axios 请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
1) GET请求
axios.get('/user?ID=12345')
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response.data);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
axios.get('/user', {
params: {
ID: 12345
}
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
2) POST请求
axios.post('/user', {
firstName: 'Fred',
lastName: 'Flintstone'
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
|
Server.js 代理
- 除了熟知的 nginx 代理,还可以用 js 实现代理。
- 代理是为了解决跨域请求,在前后端交互中,前端发给后端的请求被后端接收到,但是后端返回给前端的数据却无法被前端接收。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
export default class App extends React.Component {
getStudentData = () => {
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/api1/students').then(
(response) => {
console.log('成功了', response.data);
},
(error) => {
console.log('失败了', error);
}
);
};
getCarData = () => {
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/api2/cars').then(
(response) => {
console.log('成功了', response.data);
},
(error) => {
console.log('失败了', error);
}
);
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.getStudentData}>点我获取学生数据</button>
<button onClick={this.getCarData}>点我获取汽车数据</button>
</div>
);
}
}
//引入了 http-proxy-middleware 库,它提供了一种简单的方法来创建代理中间件。
const proxy = require('http-proxy-middleware');
module.exports = function (app) {
app.use(
proxy('/api1', {
//遇见/api1前缀的请求,就会触发该代理配置
target: 'http://localhost:5000', //请求转发给谁
changeOrigin: true, //控制服务器收到的请求头中Host的值。Host请求标识请求来源
pathRewrite: { '^/api1': '' }, //重写请求路径(必须)
}),
proxy('/api2', {
target: 'http://localhost:5001',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { '^/api2': '' },
})
);
};
|
路由
哈希路由和浏览器路由
BrowserRouter 与 HashRouter 的区别
1.底层原理不一样:
BrowserRouter 使用的是 H5 的 history API,不兼容 IE9 及以下版本。
HashRouter 使用的是 URL 的哈希值。
2.path 表现形式不一样
BrowserRouter 的路径中没有#,例如:localhost:3000/demo/test
HashRouter 的路径包含#,例如:localhost:3000/#/demo/test
3.刷新后对路由 state 参数的影响
(1).BrowserRouter 没有任何影响,因为 state 保存在 history 对象中。
(2).HashRouter 刷新后会导致路由 state 参数的丢失!!!
4.备注:HashRouter 可以用于解决一些路径错误相关的问题。
编程式路由导航
不需要用户触发,可以自动跳转链接
借助 this.prosp.history 对象上的 API 对操作路由跳转、前进、后退
-this.prosp.history.push()
-this.prosp.history.replace()
-this.prosp.history.goBack()
-this.prosp.history.goForward()
-this.prosp.history.go()
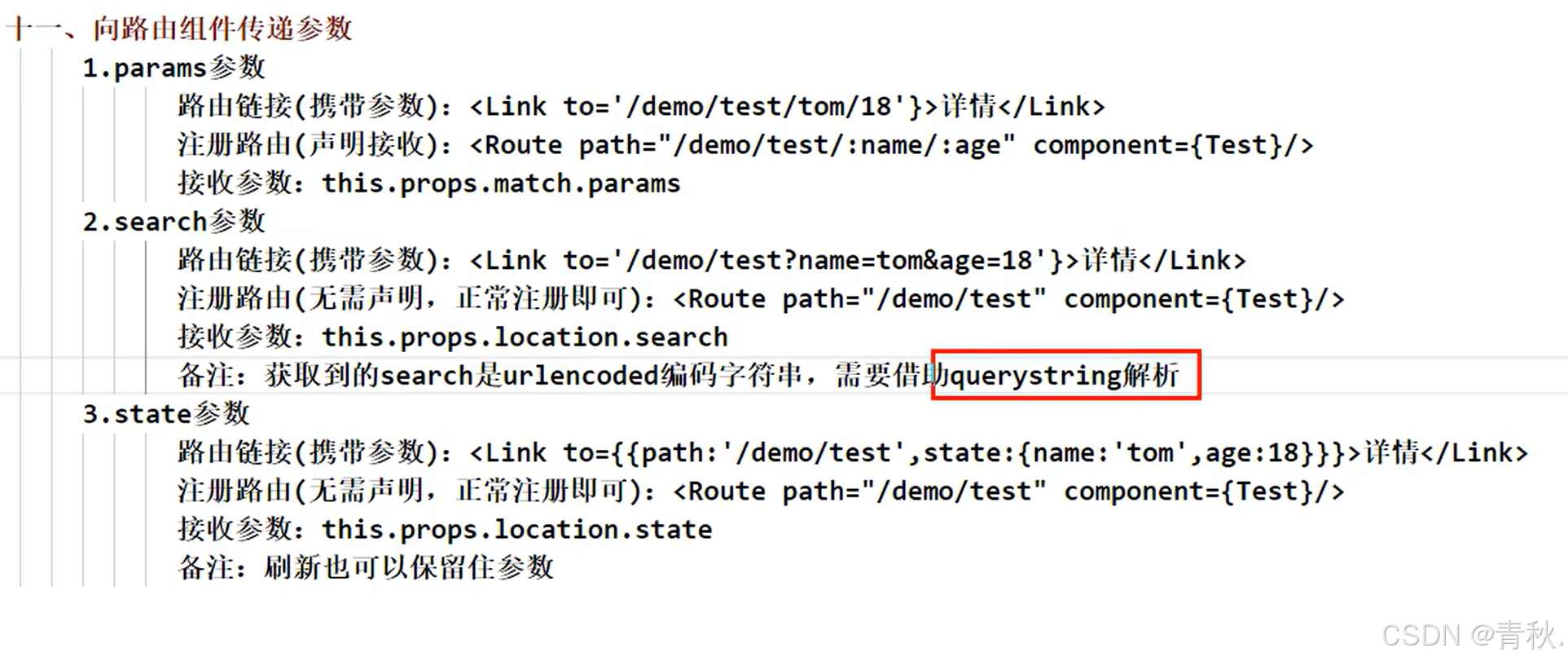
向路由组件传参

也就是说,定义的虚拟 dom 中,开头小写的标签会去 html 中寻找同名的元素并替换,找不到就会报上面的错误。如果是开头大写的标签,那么就是自定义的组件 ,如果写成 Good,那么浏览器就会去渲染 Good 组件,因此 Good 组件需要提前定义,否则会 undefined。
